Change Language :
igus® terms in alphabetical order
The glossary contains the most important abbreviations, terms, formulas, and pictograms having to do with e-chains®.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Explanation: | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| α | = | Angle of rotation | [°] |
| ΔM | = | Deviation of the centre point | [mm] |
| a | = | Acceleration | [m/s2] |
| AR | = | Outer radius, e-chains® (for twisterchain) | [mm] |
| Ba | = | e-chain® outer width | [mm] |
| Bi | = | e-chain® inner width | [mm] |
| BRa | = | Guide trough outer width | [mm] |
| BRi | = | Guide trough inner width | [mm] |
| D | = | Over length e-chain® radius in final position | [mm] |
| D2 | = | Over length for long travels gliding | [mm] |
| FLB | = | Unsupported length with sag | [m] |
| FLG | = | Unsupported straight length | [m] |
| FLU | = | Unsupported lower run | [m] |
| FZmax | = | Maximum fill weight | [kg/m] |
| H | = | Nominal clearance height | [mm] |
| H2 | = | Installation height with lowered mounting | [mm] |
| ha | = | Outer e-chain® height | [mm] |
| HF | = | Required clearance height | [mm] |
| hi | = | inner e-chain® height | [mm] |
| HRa | = | Outer trough height | [mm] |
| HRi | = | Inner trough height | [mm] |
| IR | = | Inner radius e-chain® | [mm] |
| K | = | Add-on for bend radius (K is taken from the data tables of the individual series) | [mm] |
| K2 | = | Add-on for bend radius if the mounting point is lowered (for long travels) | [mm] |
| LK | = | e-chain® length | [mm] |
| n | = | Number of links | [1] |
| nMon | = | Number of installation sets (left/right) | [1] |
| nRi | = | Number of trough sets (left/right) | [1] |
| R | = | Bend radius | [mm] |
| RBR[/sub] | = | Reverse Bend Radius | [mm] |
| S | = | Travel | [mm] |
| S/2 | = | Half length of travel | [mm] |
| T | = | e-chain® pitch | [mm] |
| v | = | Speed | [m/s] |
| X1 | = | Inner machine limit (twisterchain) | [mm] |
| X2 | = | e-chain® outer radius, including clearance | [mm] |
| Formula | Describtion | |
|---|---|---|
| SFLB = 2 * FLB | = | Calculation of maximum travel length, unsupported with sag |
| SFLG = 2 * FLG | = | Calculation of maximum travel length, unsupported straight |
| BRI ≥ Ba + 5 | = | Calculation of the minimum guide trough width |
| HRI ≥ 2 * ha | = | Minimum height of guide channel on gliding application |
| K = R * π + (2 x T) | = | Add-on for bending radius |
| LK = S/2 + ΔM + K | = | e-chain® length, fixed end outside the center of the travel distance (on FLG, FLB and ΔM) |
| LK = S/2 + K | = | e-chain® length, all installation types, fixed end in the center of the the travel distance, except circular motions and most long travel distances (on FLG, FLB) [m] |
| LK = S/2 + K2 | = | Calculation of chain lengths for long travels, fixed end in the center of travel |
Opening principle: The quick finder gives an overview of the options for filling the energy chains and energy tubes

"easy" design - simply press cables in

One-piece, non-openable

Openable from both sides - lids openable along the outer radius, from one side

triflex R – light version with "easy" design; simply press cables in

Openable from one side on the outer radius

Lids removable along the outer radius

Easy filling from both sides with "easy" design
triflex R – variant with snap-lock mechanism

Lids removable along the outer radius

triflex R – fully enclosed design, non-openable
Zipper - zip-open along the outer radius

Crossbars openable along the outer radius, from both sides

Crossbars removable along the inner and outer radius

triflex R – "easy" design; simply press cables in

Openable along the inner radius, from one side

Crossbars openable from both sides along the inner radius
Pictogram and installation methods
Unsupported
Gliding
Vertical hanging
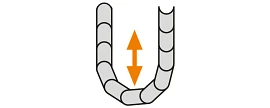
Vertical standing
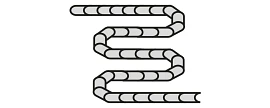
Zig-zag
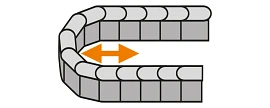
Side-mounted
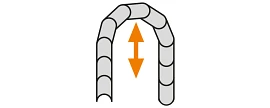
Rotary movement
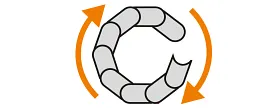
Horizontal and vertical
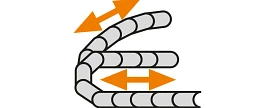
Nested
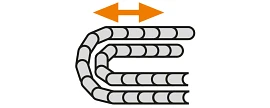
Side by side
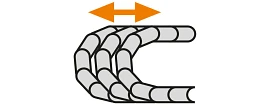
Combined motion
Discuss your project with an expert!
Whether you're interested in end-to-end, fully assembled solutions or looking to build your own customizable project, let us assist you with a solution based on your specific application and requirements. Contact us via the form below or call us at (800) 521-2747 to discuss your project today!